Exploring the World of Programming: Micro:bit, Arduino and Raspberry Pi
The world of electronics and programming offers a range of platforms tailored to different skill levels and project requirements. Among the most popular are the Micro:bit, Arduino, and Raspberry Pi. Each of these platforms has unique features, capabilities, and target audiences. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between these three platforms and examine their various use cases.
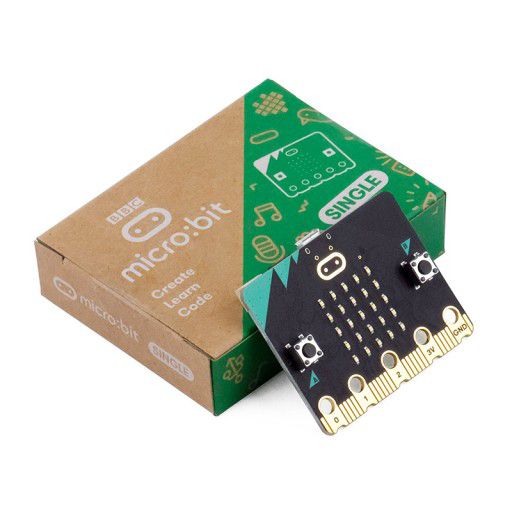
| MICRO:BIT Overview The BBC Micro:bit is a pocket-sized computer designed to introduce kids and beginners to coding and electronics. It is widely used in educational settings for its simplicity and ease of use. |
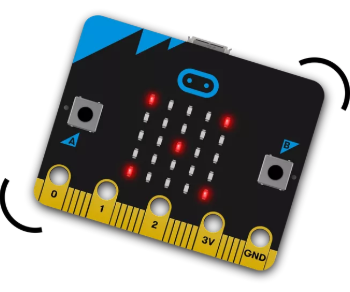 |
Key Features
|
|
Use Cases
|
 |
ARDUINO Overview Arduino is an open-source electronics platform based on easy-to-use hardware and software. It is widely used by hobbyists, makers, and professionals for a wide range of projects. |
Key Features
|
|
Use Cases
|
| RASPBERRY PI Overview Raspberry Pi is a small, affordable computer capable of running a full-fledged operating system. It is designed to promote computer science education and is also popular among makers and developers. |
 |
Key Features
|
|
Use Cases
|
Key Differences
| MICRO:BIT | ARDUINO | RASPBERRY PI | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target Audience | Primarily for beginners and educational purposes. | Hobbyists, makers, and more advanced users. | Developers, educators, and hobbyists looking for a full computing experience. | |
| Complexity | Simplest to use, with a gentle learning curve. | Moderate complexity, requiring some understanding of electronics and programming. | Most complex, essentially a full computer requiring knowledge of operating systems and networking. | |
| Expandability | Limited expandability, designed as a standalone educational tool. | Highly expandable with numerous shields and modules. | Also highly expandable, with the ability to run a variety of software and connect numerous peripherals. |
Micro:bit, Arduino, and Raspberry Pi each offer unique advantages depending on the user’s experience level and project requirements. The Micro:bit
is perfect for beginners and educational purposes, providing an easy entry into the world of coding and electronics. Arduino offers greater flexibility and
is ideal for a wide range of DIY electronics projects. Raspberry Pi, with its full computer capabilities, opens up possibilities for more advanced projects,
from desktop computing to complex IoT applications. By understanding the strengths of each platform, users can choose the best tool for their specific needs
and unlock their creativity in the world of electronics and programming.